Endoscopic Ultrasound Terminology
Echogenicity of the tissue refers to the ability to reflect or transmit US waves in the context of surrounding tissues. Whenever there is an interface of structures with different echogenicities, a visible difference in contrast will be apparent on the screen. Based on echogenicity, a structure can be characterized as anechoic, hypoechoic and hyperechoic.
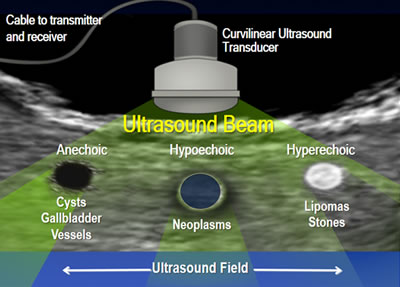
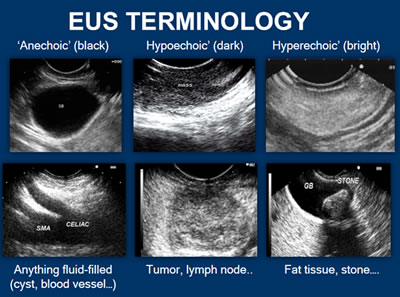
- Anechoic: Structures appear black, meaning no internal echoes. Examples include cysts, vessels, gallbladder ascites and water.
- Hypoechoic: Gives off fewer echoes; they are darker than surrounding structures. Examples include lymph nodes and tumors.
- Hyperechoic: Increased density of sound waves compared to surrounding structures. Examples include bone and fat calcifications.
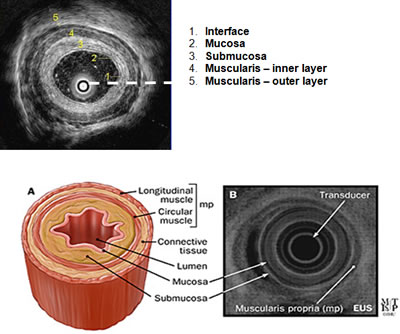
Take a look at the example of a cross-section of the esophagus. On endoscopic ultrasound (radial), the gastrointestinal wall appears as five layers:
- The first layer is hyperechoic and corresponds to the superficial mucosa.
- The second layer is hypoechoic and corresponds to the deep mucosa.
- The third layer is hyperechoic and corresponds to the submucosa plus the acoustical interface between the submucosa and the muscularis propria.
- The fourth layer is hypoechoic and corresponds to the muscularis propria minus the acoustical interface between the submucosa and the musclaris propria.
- The fifth layer, the serosa and subserosal fat, is hyperechoic.
Next Page: Radial vs. Linear EUS
2 of 10

